Annual Survey of Exercise Professionals Celebrates 20-Year Anniversary
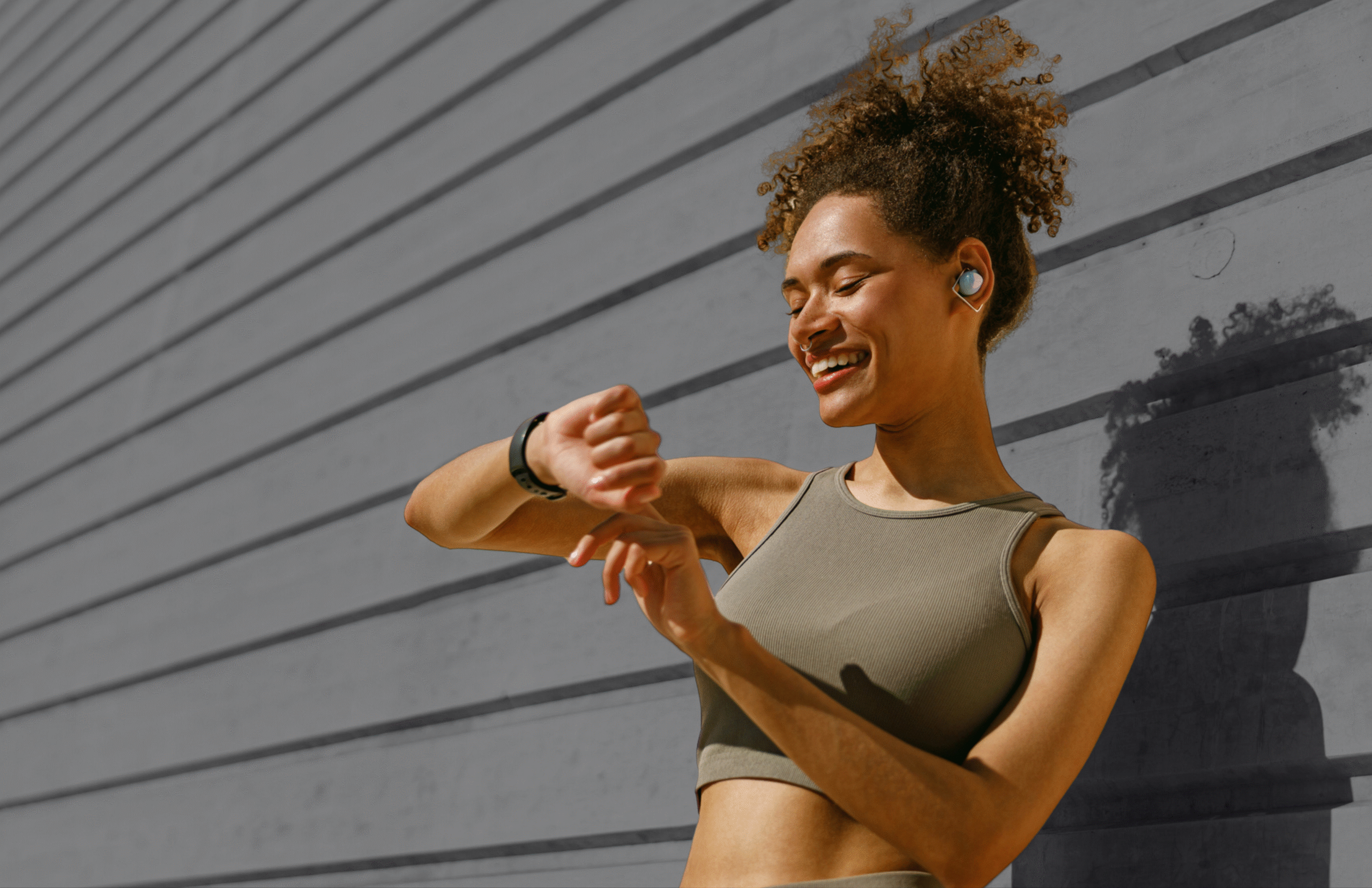
For the 20th year, the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) has published its annual Worldwide Fitness Trends forecast, and the number one trend for 2026 is Wearable Technology. The report, based on a survey of 2,000 clinicians, researchers and exercise professionals in the fitness industry, was published today in the November/December issue of ACSM’s Health & Fitness Journal®.
“We’ve seen dramatic changes in fitness trends over the last two decades, and this milestone gives us a long-term perspective of how the field has evolved and impacted health and fitness” said Cayla R. McAvoy, PhD, ACSM-certified exercise physiologist, lead author of 2026 ACSM Worldwide Fitness Trends: Future Directions of the Health and Fitness Industry. “Over the years, we’ve seen fitness trends tied to childhood obesity, online training during the COVID pandemic, addressing mental health, the rise of fitness technology, medically integrated programs and active aging.”
The annual trends report helps exercise professionals, gym owners and their clients understand the findings in relation to their own work environment. Whether refining services in a fitness club, adapting training programs to meet specific health and fitness needs, shaping physical activity policies or researching implementation and impact, the results offer practical guidance to inform decision-making. Survey findings offer both a snapshot of current practices and insight into new priorities and growth areas across the health and fitness industry.
Rounding out the top five fitness trends after Wearable Technology are Fitness Programs for Older Adults, Exercise for Weight Management, Mobile Exercise Apps, and Balance, Flow and Core Strength.
Commenting on Wearable Technology as the #1 fitness trend for 2026, McAvoy said “Nearly half of U.S. adults now own a fitness tracker or smartwatch, so the question is no longer whether people will use wearables. What matters now is teaching people how to use them in ways that best support their health and behavior change.”
New to the 20th anniversary trends report:
- Practical applications for each of the 20 trends on the list. These applications address practice, programming or policy and are intended to help interpret not only which trends are gaining momentum but also how they can be applied in real-world settings.
- Fitness terminology has changed over the last two decades. The definition of trend has evolved to signify a widely adopted and/or sustained pattern in health and fitness participation, professional practice or industry offerings. Unlike fads, trends persist beyond temporary enthusiasm and demonstrate measurable engagement, market presence, or long-term impact. The trend of “Exercise for Weight Loss” has been renamed “Exercise for Weight Management” to reflect a broader range of goals, including weight loss, maintenance and gain.
- Adult Recreation and Sport Clubs made its first appearance on the list of top trends, influenced by the popularity of Pickleball and a desire for social connection while exercising.
Here are the top 10 trends for 2026, with expert commentary from the authors (including video) and practical applications for exercise professionals and the public:
#1 Wearable Technology:
Consistently a top trend over the last several years, Wearable Technology continues to evolve with advanced biosensors now capturing indicators such as fall or crash detection, heart rhythm, blood pressure, blood glucose and skin temperature. These are particularly important for a wide demographic, ranging from patients in rehabilitation, fitness beginners, athletes and aging adults. This trend held a top three rank in nearly all professions and age groups surveyed, reflecting its widespread appeal.
Application: As wearable technologies evolve, exercise professionals must stay informed about differences in device accuracy and user experience. Although guidelines exist for evaluating wearables, rapid innovation often outpaces validation. Still, these tools can meaningfully support self-monitoring, accountability and sustained engagement. When applied with intention, wearables enhance individualized coaching and help reinforce healthy habits over time.
Expert Commentary:
“Nearly half of U.S. adults now own a fitness tracker or smartwatch, so the question is no longer whether people will use wearables. What matters now is teaching people how to use them in ways that best support their health and behavior change.” Cayla R. McAvoy, PhD, ACSM-EP, EIM (Video Version)
“Wearable technology is a powerful tool to track fitness and health. While some data is useful and accurate, some metrics may be experimental or unreliable. Data is often useful for tracking patterns or changes over time, and certified exercise professionals can provide support on how to interpret the information.” – Sarah M. Camhi, PhD, FACSM, ACSM-EP, EIM
#2 Fitness Programs for Older Adults (active aging):
The baby boomer generation includes 73 million Americans, all of whom will be over age 65 by 2030, intensifying demand for age-appropriate, evidence-based exercise options. According to the 2023 IHRSA U.S. Health & Fitness Consumer Report, adults 65 and older now visit gyms and studios more often than any other age group.
Application: This ranking, along with recent industry data, points to growing engagement and opportunity within this population. A 2024 industry report found that programs labeled “low intensity,” “functional,” or “active aging” consistently attract more participants than those called “senior fitness.” These findings suggest rising demand and participation, though thoughtful program plans, instructor training and accessibility remain essential to designing effective offerings for older adults. Particularly useful approaches for this population include resistance training to preserve strength, balance and mobility exercises to reduce fall risk, and low-impact cardiovascular activity to support heart health.
Expert Commentary:
“Physical activity is especially critical for older adults, as evidence consistently links regular exercise to the prevention and management of age-related conditions. Effective programs should be safe, enjoyable, and designed to enhance functional capacity in Activities of Daily Living.”
– Jennifer Turpin Stanfield, MA, ACSM-EP (Video Version)
“The older adult population will soon be the largest in U.S. history and will require qualified exercise professionals to provide safe and effective exercise for this group of people. The rank of this trend indicates the importance of better understanding how to serve this population in our industry.” – Paul M. Gallo, EdD, FACSM, ACSM-CEP, ACSM-EP, ACSM-GEI, EIM, editor-in-chief of ACSM’s Health & Fitness Journal (Video Version)
#3 Exercise for Weight Management:
Its highest position to date, the Exercise for Weight Management trend now includes increases in the use of obesity management medications such as GLP-1 RA. Obesity affects 42.4% of U.S. adults, while approximately 49% of those with obesity report actively trying to manage their weight.
Application: Exercise remains essential to long-term weight management by supporting lean mass, physical function, and metabolic health. Research shows that individuals who continue to exercise during pharmacologic treatment maintain greater fat loss and preserve lean mass after stopping medication than those using medication alone. Exercise professionals should consistently reinforce the unique role of exercise in sustainable weight outcomes and position themselves as trusted partners in this process.
Expert Commentary:
“The efficacy of exercise in combating the obesity epidemic is well-documented. Exercise should be considered a fundamental component of the treatment and management strategy.”
– Alexios Batrakoulis, PhD, FACSM, ACSM-EP, ACSM-CPT (Video Version)
“Exercise and physical activity should be part of any weight management program due to their positive impact on both mental and physical health. Weight loss drugs may reduce muscle, which can harm health. Exercise may preserve muscle, boost strength, and improve physical function, but research is still ongoing.”
-Sarah M. Camhi, PhD, FACSM, ACSM-EP, EIM
#4- Mobile Exercise Apps
Mobile Exercise Apps deliver on-demand, scheduled, live-streamed, or recorded workouts, offering users convenience and flexibility to exercise anytime, anywhere. In 2024, more than 345 million people used fitness apps, generating more than 850 million downloads. App users tend to be younger, female, college-educated, and living in urban areas, with lower adoption observed among older adults and individuals with limited digital literacy.
Application: Mobile apps can promote exercise adherence by offering convenience, structure, and self-monitoring tools. Research shows users value features that support goal setting and progress tracking, which may drive sustained engagement. Apps with habit-forming elements such as reminders, rewards, or social features may further support long-term use. While short-term improvements in physical activity have been demonstrated, more research is needed to understand long-term outcomes. Exercise professionals can leverage apps as supplemental tools, particularly for clients who prefer flexible, tech-enabled fitness options.
Expert Commentary:
“The widespread use of smartphones and wearables has made mobile exercise apps highly accessible. These apps can track activity, support goal setting, provide on-demand classes, and facilitate social competition, making them a promising tool for promoting regular physical activity. Their overall effectiveness, however, depends on user engagement and program quality.” Jennifer Turpin Stanfield, MA, ACSM-EP (Video Version)
#5. Balance, Flow, and Core Strength
After a pandemic-related dip in group participation, these formats have regained momentum alongside increased interest in holistic health and mind–body integration. This trend has been reframed as a key component of a balanced fitness regimen, bridging movement quality with mental well-being.
Application: Exercise professionals can integrate these formats to help clients improve posture, mobility and core control, which supports safer movement during strength and cardio training. Accordingly, research highlights the importance of such formats on improving movement control and injury prevention, especially in the aging population.
Expert Commentary:
“The rise of trends like core training, balance, and flow makes perfect sense given the growing popularity of Pilates and barre. These formats allow trainers to provide one-on-one attention within a group setting, delivering both personalized support and opportunities to deepen the mind-body connection. Building strength in the core, improving balance, and engaging in mindfulness-based training are key to overall movement quality, injury prevention, and long-term health.” – Rachelle Reed, PhD, ACSM-EP (Video Version)
“Pilates, yoga, and core training are resonating across generations. Their popularity reflects a broader industry shift toward longevity, holistic health, and mind-body integration.”
– Cayla R. McAvoy, PhD, ACSM-EP, EIM (Video Version)
#6. Exercise for Mental Health
This trend’s rank is up two spots from last year. Each year in the U.S., more than one in five adults report experiencing a mental health condition, reinforcing the importance of movement-based strategies that support emotional well-being. One national survey found that 78% of exercisers cite mental or emotional well-being as their top reason for working out, ahead of physical fitness or appearance goals. Exercise offers an evidence-based, practical and scalable approach to improving mental health in both preventive and adjunctive contexts.
Application: While a need exists for exercise-based programs that positively address mental health, many gyms and studios do not explicitly promote these outcomes. Framing exercise around mental health benefits may better align programs with motivation and support long-term engagement. Certain formats may be especially appropriate for supporting mental health outcomes: resistance training reduces depressive symptoms, while low-intensity, mindfulness-based formats such as yoga may offer additional value for stress reduction and emotional well-being.
Expert Commentary:
“Exercise is now being embraced as much for the mind as for the body, serving as a go-to strategy for stress relief, mood, and resilience. National surveys show that mental well-being is the top reason people choose to exercise, ranking ahead of fitness or appearance.” – Cayla R. McAvoy, PhD, ACSM-EP, EIM (Video Version)
“Regular exercise is one of the most effective strategies we have to improve mental health, build emotional resilience, and enhance overall-wellbeing. Its impact could rival some traditional clinical interventions and is certainly a strong supportive intervention. This holds true not only for the general populations, but also for vulnerable groups such as pregnant women, youth, and older adults.”
– A’Naja M. Newsome, PhD, ACSM-CEP, EIM
#7 Traditional Strength Training
Despite its benefits, fewer than 30% of U.S. adults meet the recommended guidelines for muscle-strengthening activity. Resistance exercises use free weights such as barbells, dumbbells and kettlebells to improve muscular strength, endurance and function. It plays a key role in maintaining bone density, metabolic health, and mobility across the lifespan.
Application: Exercise professionals can address existing participation gaps by offering strength training programs that are progressive, inclusive and accessible to diverse populations. Messaging should emphasize long-term health benefits and functional outcomes, not just aesthetics or performance. To improve uptake, strength training can be integrated into group classes, low-cost programs or hybrid formats that reduce intimidation and promote consistency.
Expert Commentary:
“Strength training has been thoroughly researched and has gained significant popularity as one of the most effective fitness strategies due to its proven effectiveness, safety, and appeal to individuals of all ages and fitness levels.” – Alexios Batrakoulis, PhD, FACSM, ACSM-EP, ACSM-CPT (Video Version)
#8. Data-Driven Technology:
More than 70% of wearable users have reported applying their output data to inform exercise or recovery strategies, and exercise professionals can use biofeedback to tailor intensity, assess readiness and reduce risk of overtraining.
Application: A 2023 study found that athletes who used Heart Rate Variability (HRV)-guided training improved performance and reduced injury rates compared to those using fixed programming. Regardless of fitness level, clients can benefit from personalized adjustments that align training with recovery status. Effective application requires translating raw data into actionable insights, communicating clearly with clients, and designing programs that align with individual goals and readiness.
Expert Commentary:
“Biofeedback has become an impactful tool – allowing both clients and exercise professionals the ability to personalize exercise while gaining real time insights to the body’s physiological response. In combination with wearable technology, data-driven technology can help in transforming exercise training into a more tailored, and responsive experience.” – Jessica Sansone, PhD, ACSM-EP, EIM (Video Version)
“Real-time physiological data, such as heart rate variability and sleep patterns, is shaping how people train and recover. These tools allow for more personalized adjustments that improve results and reduce injury risk. The key is translating complex numbers into clear, actionable guidance.”
– Cayla R. McAvoy, PhD, ACSM-EP, EIM (Video Version)
#9. Adult Recreation and Sport Clubs
New to the top 20 in 2026, this trend reflects growing interest in activities that combine fitness with fun, flexibility and social connection outside traditional gym settings. The rising popularity of Pickleball, clubs and leagues involving less strenuous activities are examples of this trend.
Application: By emphasizing enjoyment, camaraderie and consistent participation, adult recreation and sport clubs may help reduce barriers to exercise and improve long-term adherence. Group-based formats can be particularly effective for adults who are otherwise inactive, especially those motivated by connection or casual competition. Exercise professionals can support participation by integrating recreation-based programs into their offerings, leading community groups or collaborating with local leagues to reach adults who may not engage through traditional gym settings.
Expert Commentary:
“Pickleball, running clubs and adult leagues are bringing people back to exercise in fun, social ways. These activities are about connection as much as they are about fitness.”
– Cayla R. McAvoy, PhD, ACSM-EP, EIM (Video Version)
#10. Functional Fitness Training
The “fitness is function” movement rounds out the top 10. Functional Fitness Training includes strength, power, mobility and endurance movements designed to improve physical performance in real-world activities. Versatility makes it appropriate for youth, adults, older and athletic populations alike. Programs often emphasize movements such as squats, lunges and carries that transfer directly to daily life or sport.
Application: Professionals can use functional training to improve joint stability, mobility, and sport-specific performance. Although often associated with older adults or injury rehabilitation, functional training also benefits athletic populations, as evidence shows improvements in strength, speed, power, and balance among athletes. Functional Fitness Training can be delivered with or without equipment and adapted to individual sessions, group formats, or hybrid models that prioritize movement efficiency and functional capacity over aesthetics or volume.
Expert Commentary:
“Functional Fitness Training has emerged as a compelling solution for enhancing musculoskeletal health and achieving fitness goals, while offering enjoyment and motor control for individuals of all ages and abilities.”
– Alexios Batrakoulis, PhD, FACSM, ACSM-EP, ACSM-CPT (Video Version)
“Functional fitness marks a shift toward movement-based health supporting independence in older adults, translating strength into everyday capability and reinforcing the preventive power of exercise. It is not just a trend, but a cornerstone of exercise prescription.” – A’Naja M. Newsome, PhD, ACSM-CEP, EIM
More detail, including the full list of top 20 trends, is available in the article.
Additional resources to help tell your story:
- Webpage: 2026 Fitness Trends Resource Page
- Video: Top 10 Trends Over 20 Years
- Infographic: 2026 Top 10 Fitness Trends
- Supplemental Article: Employer Perspective
- Supplemental Article: International Commentary of the Worldwide Survey of Fitness Trends
- Table: Top 10 Yearly Comparison (2007-2026)
- Cover Art: Worldwide Fitness Trends 20th Anniversary Issue
- Video Quotes: For Online and Broadcast Stories
Media Contact: Paul Branks, ACSM Chief Communications Officer | pbranks@acsm.org